
SDG 13.2 Low-carbon energy use
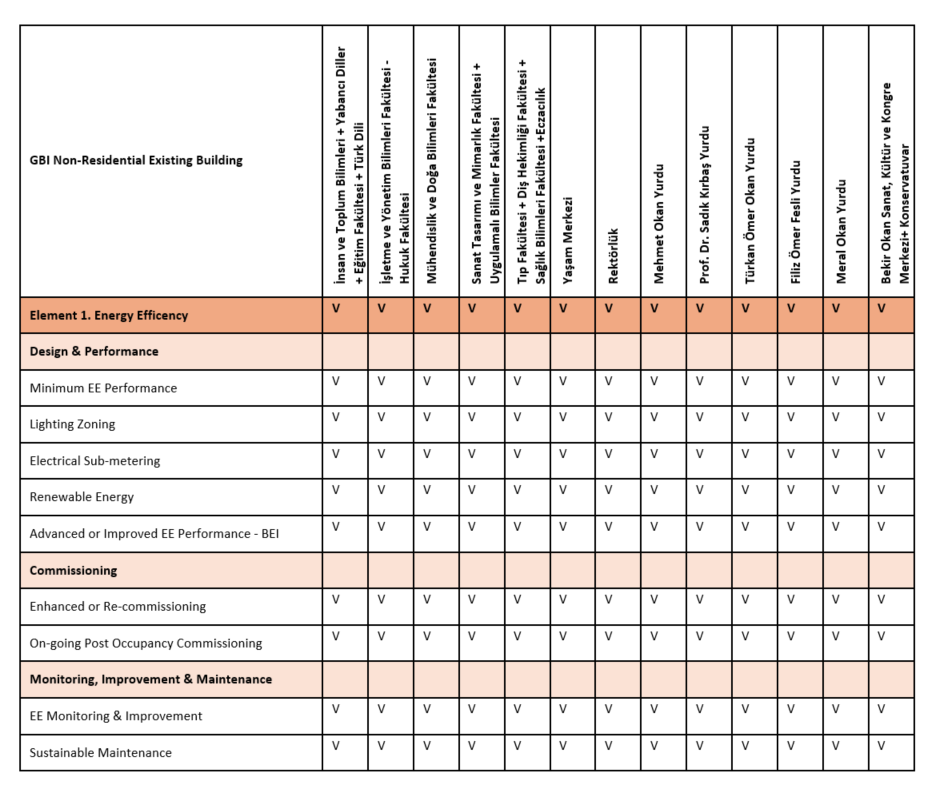
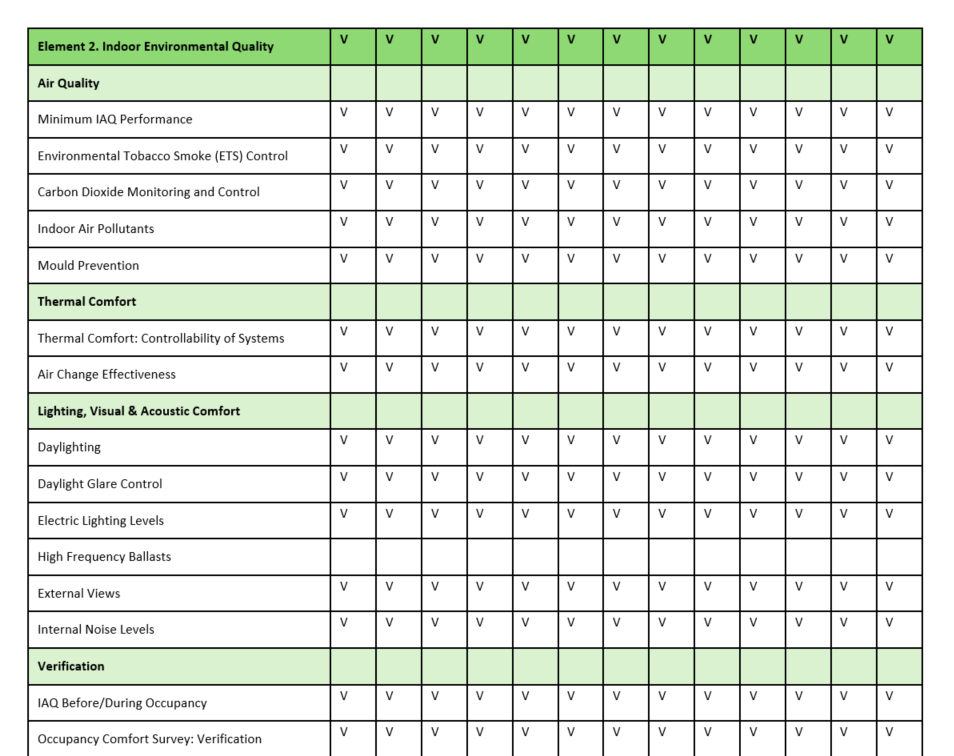
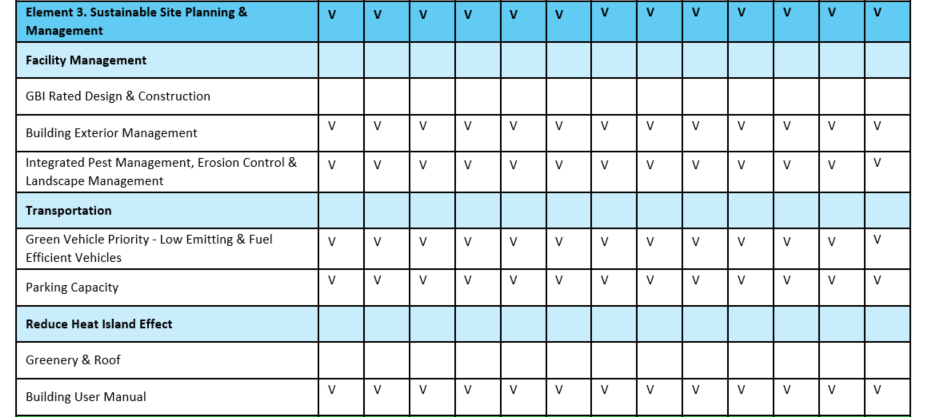
Istanbul Okan University prioritizes sustainability and energy efficiency across all its campuses. Energy-efficient devices and systems are widely used in both academic and administrative buildings.
Through these practices, the university continues to reduce its carbon footprint and support long-term energy management strategies.
Building Automation (B1, B2)
Security (S1, S2, S3, S4)
Energy (E1, E2)
Water (A1, A2)
Indoor Environment (I1, I2, I3, I4)
Lighting (L1, L2, L3, L4)
Example of Energy Efficient Appliances Usage: (Istanbul Okan University, Türkiye)
SDG 13.2.1 Low carbon energy tracking
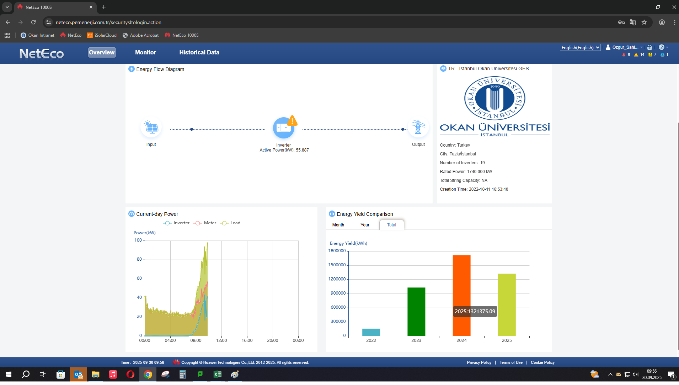
Istanbul Okan University measures the amount of low-carbon energy used across the entire university. In line with its sustainability commitment and its goal of reducing its carbon footprint, the university actively monitors energy consumption to assess the use of renewable and low-carbon energy sources. These data are used to inform energy management strategies and to support efforts aimed at further reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
 |  |
 | |
| Solar Energy Monitoring (Istanbul Okan University, Türkiye) | |
There are two systems: solar panels and a wind turbine.
| Total Solar Energy Produced kWh (Istanbul Okan University, Türkiye) | ||
| 2023 | 2024 | |
| 994888 | 1713151.11 | |
| Example of Total Electricity Usage ( Istanbul Okan University, Türkiye) | |
| Year | Total Amount of Electricity Usage (kWh) |
| 2022 | 5487187 |
| 2023 | 3987753 |
| 2024 | 4006982 |
SDG 13.2.2 Low-carbon energy use
 |  |
 |  |
| Example of Roof Solar Panels (Istanbul Okan University, Turkiye) | Example of Wind Turbine (Istanbul Okan University, Turkiye) |
 |  |
 | |
| Solar Energy Monitoring (Istanbul Okan University, Türkiye) | |
 | |
SDG 13.3 Environmental education measures
 | |
| Copy of the Istanbul Okan University ISO50001 certification (Istanbul Okan University, Türkiye ) |
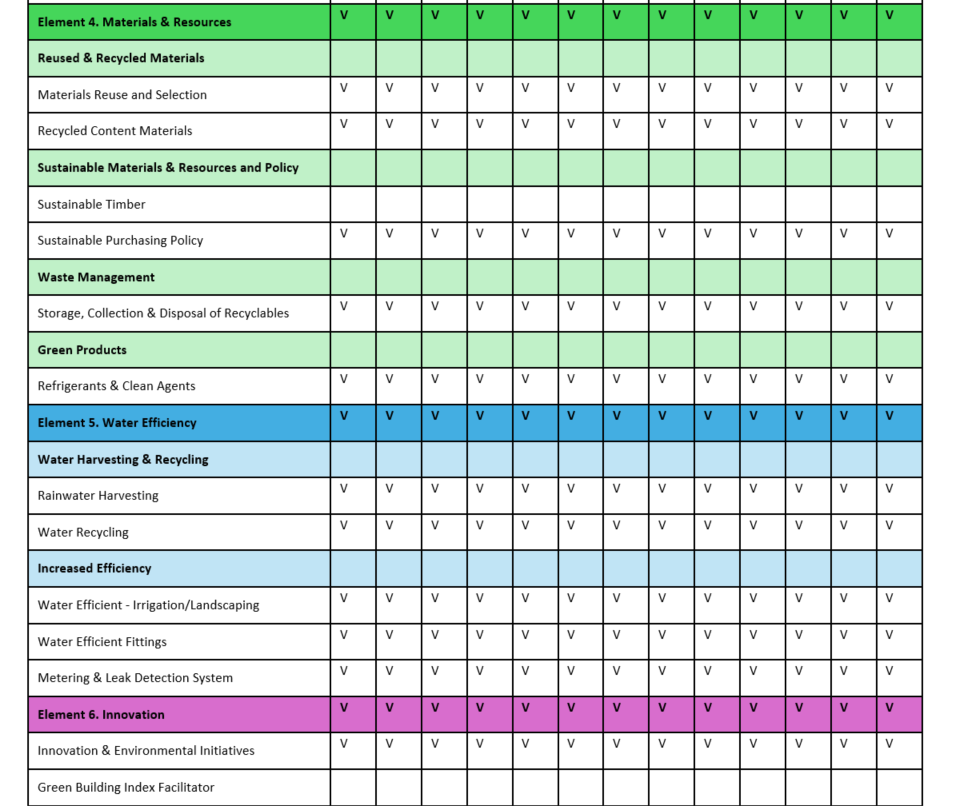
SDG 13.3.1 Local education programmes on climate
Istanbul Okan University offers local education programs and campaigns focused on climate change risks, impacts, mitigation, adaptation, and impact reduction. The university engages with students, academic staff, and the wider community by organizing workshops, seminars, and awareness campaigns to promote understanding of climate change–related issues. These initiatives aim to educate and empower individuals to address climate change and its associated challenges.
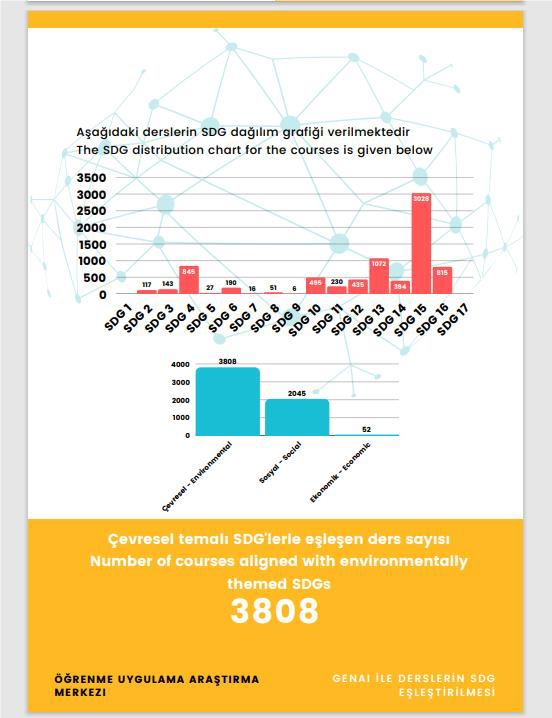
Sustainability courses at Istanbul Okan University
Academic Programs:
Research and Projects:
Management and Campus Practices:
Community Contribution and Collaboration:
SDG 13.3.2 Climate Action Plan, shared
Istanbul Okan University has a Climate Action Plan that is shared with local authorities and community groups. This plan outlines the university’s strategies to reduce its carbon footprint, promote sustainability, and collaborate with external stakeholders to address climate-related challenges. This initiative reflects the university’s commitment to contributing to broader societal climate goals and supporting collective action.
SDG 13.3.3 Co-operative planning for climate change disasters
Istanbul Okan University participates in collaborative planning for climate change–related disasters, including those that lead to the displacement of people both domestically and across borders. The university works in cooperation with government agencies and relevant organizations to develop strategies and response plans for such emergencies, reflecting its commitment to addressing the human and social impacts of climate change. This collaboration helps ensure a coordinated and effective response to climate-related challenges and disasters.
YÖK Earthquake-Affected Student
SDG 13.3.4 Inform and support government
Istanbul Okan University informs and supports local and regional authorities on early warning and monitoring of climate change–related disaster risks. The university collaborates with authorities by sharing research, data, and expertise, contributing to enhanced community preparedness and response capacities. This cooperation supports the development of resilient local infrastructure and helps mitigate the impacts of climate-related disasters.
SDG 13.3.5 Environmental education collaborate with NGO
Istanbul Okan University collaborates with non-governmental organizations (NGOs) to support climate change adaptation. The university partners with various NGOs to implement projects, share research, and develop strategies aimed at adapting to the impacts of climate change. These collaborations are part of the university’s commitment to promoting sustainability and supporting societal resilience in the face of environmental challenges.

 |  |
| Examples of Sustainability-Related Activities (Istanbul Okan University, Türkiye) | |
 | |
 | |
SDG 13.4.1 Commitment to carbon neutral university
Istanbul Metropolitan Municipality (IMM) has taken significant steps in combating climate change. Local governments came together at the C40 Mayors Summit held in Copenhagen to advance this goal. The Mayor of Istanbul, Ekrem İmamoğlu, along with other signatory leaders, signed the “Deadline 2020” Commitment. In line with this commitment, IMM has initiated actions to achieve the goal of making Istanbul a “resilient city” and a “carbon-neutral city” by 2050. As an integral part of Istanbul, our university is also included in these objectives.
Istanbul Okan University is committed to becoming a carbon-neutral institution in order to contribute globally to the fight against climate change. In line with this commitment, the university actively works to reduce carbon emissions across all sectors, including energy use, transportation, waste management, and consumed materials. Acting in parallel with Istanbul Metropolitan Municipality’s goal of becoming a carbon-neutral city by 2050, we acknowledge our responsibility to be a key actor in Istanbul’s environmental transformation.
Our efforts focus on integrating sustainable practices into campus operations, fostering a culture of sustainability among students and staff, and collaborating with stakeholders such as government bodies, non-governmental organizations, and the wider community. Through continuous innovation, research, and education, Istanbul Okan University aims to play an active role in ensuring a resilient and low-carbon future.
Istanbul Metropolitan Municipality (IMM) has taken significant steps in combating climate change. Local governments came together at the C40 Mayors Summit held in Copenhagen to advance this objective. The Mayor of Istanbul, Ekrem İmamoğlu, along with other signatory leaders, signed the “Deadline 2020” Commitment. In line with this commitment, IMM has initiated actions aimed at achieving the goals of making Istanbul a “resilient city” and a “carbon-neutral city” by 2050. As an integral part of Istanbul, our university is also included within these goals.
Istanbul Okan University is committed to becoming a carbon-neutral institution in order to contribute globally to the fight against climate change. In line with this commitment, the university actively works to reduce carbon emissions across all sectors, including energy use, transportation, waste management, and consumed materials. Acting in parallel with Istanbul Metropolitan Municipality’s objective of becoming a carbon-neutral city by 2050, we acknowledge our responsibility to be a key actor in Istanbul’s environmental transformation.
Our efforts focus on integrating sustainable practices into campus operations, fostering a culture of sustainability among students and staff, and collaborating with stakeholders such as government bodies, non-governmental organizations, and the wider community. Through continuous innovation, research, and education, Istanbul Okan University aims to play an active role in ensuring a resilient and low-carbon future.
SDG 13.4.2 Achieve by