
SDG 12.2 Operational measures
SDG 12.2.1 Ethical sourcing policy
Istanbul Okan University has adopted an ethical procurement policy in the supply of food and materials. The University is committed to promoting sustainability and social responsibility principles and ensures that the food and materials it procures comply with ethical standards. This includes prioritizing suppliers who adhere to fair trade practices, environmentally friendly production methods, and humane treatment of workers and animals. In addition, the University encourages the use of locally sourced and organic products in order to support local economies and reduce its environmental footprint. This policy is part of Istanbul Okan University’s broader commitment to sustainability and ethical practices.
The University places great importance on ensuring that the companies from which it procures goods and services fulfill their responsibilities toward their employees in line with the ethical procurement policy. In particular, within the framework of Occupational Health and Safety Law No. 6331, the technical specifications and contracts for procured goods and services include the following provisions pursuant to Article 4 of the Law:
The contractor is responsible for ensuring the occupational health and safety of its employees at its own expense. This includes enabling employees to benefit from occupational safety experts, workplace physicians, and, if necessary, other health personnel.
Employees’ health monitoring must be carried out, occupational risks must be prevented, and the necessary training and information must be provided. All required measures must be taken, and the organizations to be established, tools and equipment to be provided, and health and safety precautions must be adapted to changing conditions. In cases of non-compliance with occupational health and safety measures, inspection, supervision, and corrective actions must be ensured by the contractor.
Furthermore, it is carefully monitored that the contractor does not employ uninsured workers, and compliance with Social Insurance and General Health Insurance Law No. 5510 is ensured through correspondence with the Social Security Institution (SSI/SSK). Istanbul Okan University also provides Occupational Health and Safety training to personnel under its own supervision.
Through these measures, Istanbul Okan University ensures that compliance with both its ethical procurement policy and occupational health and safety regulations is meticulously observed throughout the procurement process.
SDG 12.2.3 Policy waste disposal – hazardous materials
Istanbul Okan University has established a comprehensive directive and process for waste disposal, which also includes the management of hazardous materials. The University is committed to ensuring that all wastes are disposed of in line with environmental regulations and sustainability practices. This includes the safe handling, storage, and disposal of hazardous materials such as chemicals, biological waste, and other potentially harmful substances. The University follows strict protocols to minimize environmental impact and to ensure the safety of the campus community. Regular audits and trainings are carried out to ensure compliance and to promote best practices in waste management.
Istanbul Okan University manages toxic and hazardous wastes generated on campus in accordance with the Zero Waste Regulation and relevant national legislation.
1. Types of Toxic Waste
2. Segregation and Storage
3. Safe Disposal
4. Training and Awareness
Istanbul Okan University ensures that toxic wastes are segregated at the source, safely stored, and disposed of through licensed companies in compliance with national regulations.
 |  |
 |  |
| Toksik Atık İşlemine Örnek (İstanbul Okan Üniversitesi, Türkiye) | |
Medical and biomedical wastes generated in the University’s health units and laboratories are regularly collected and processed at licensed medical waste disposal facilities using sterilization and incineration methods.
Battery wastes are accumulated in designated collection boxes across the campus and then delivered to authorized battery recycling companies for recycling or safe disposal.
Through these efforts, Istanbul Okan University ensures that toxic wastes are managed safely and in an environmentally responsible manner; by reducing the amount of hazardous waste generated each year, the University continues its progress toward its Zero Waste policy.
SDG 12.2.4 Policy waste disposal - landfill policy
Istanbul Okan University has a directive for waste disposal that includes measuring the amounts of waste sent for disposal and recycled. The University is committed to reducing its environmental impact by monitoring and tracking its waste disposal practices. This policy enables the University to actively measure and record the quantities of waste generated, with a focus on increasing recycling rates and minimizing the amount of waste sent to landfill. Regular evaluations and reporting help the University continuously improve its sustainability efforts in waste management.
The main Zero Waste activities implemented at Istanbul Okan University are as follows:
Thanks to these efforts, Istanbul Okan University not only fulfills its legal obligations but also contributes to its vision of a sustainable campus. The University views waste management not only as an environmental responsibility but also as a social responsibility.
Paper and Plastic Waste Collection in Turkey
Legal Framework
Paper and plastic wastes are regulated under the Regulation on the Control of Packaging Waste and the Zero Waste Regulation. Municipalities are generally responsible for ensuring the segregation of paper, cardboard, plastic, and other packaging wastes at the source, often in cooperation with licensed recycling companies.
Collection Practices
Processing of Waste
Nationwide Initiatives
Istanbul Okan University actively participates in nationwide paper waste collection efforts carried out in Turkey within the framework of the Regulation on the Control of Packaging Waste and the Zero Waste Regulation. The University ensures that students, academic staff, and administrative personnel segregate paper waste at the source by providing paper recycling bins in all academic and administrative buildings. The collected paper is managed in cooperation with licensed recycling companies and incorporated into the recycling system to be transformed into new paper, cardboard, packaging materials, or industrial products.
This approach both reduces natural resource consumption and the environmental impact of landfill sites, and supports the development of a responsible waste-management culture on campus. In addition, by aligning its practices with social responsibility campaigns and awareness programs, the University strengthens its sustainability and environmental responsibility principles.
SDG 12.2.5 Policy for minimisation of plastic use
Istanbul Okan University has policies aimed at reducing plastic use. As part of its broader sustainability goals, the University is committed to lowering plastic consumption on campus. This includes encouraging the use of reusable alternatives, reducing single-use plastics in dining areas and at events, and supporting awareness campaigns to minimize plastic waste. The University also collaborates with suppliers to reduce plastic packaging and promotes recycling initiatives to manage plastic waste effectively. These efforts align with the University’s commitment to environmental responsibility and sustainability.
Measures to Reduce Plastic Use
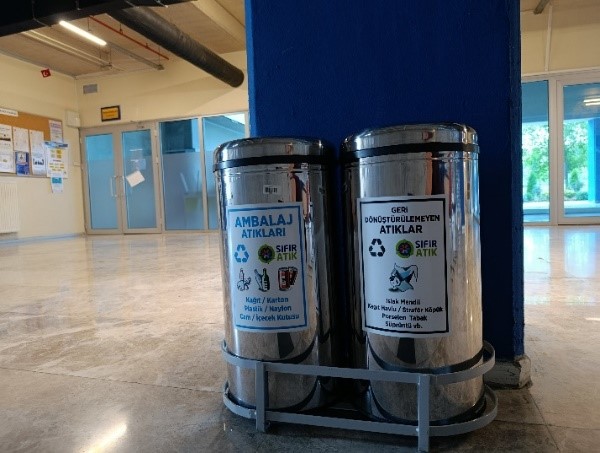 |  |  |
SDG 12.2.6 Policy for minimisation of disposable items
Istanbul Okan University has policies aimed at reducing the use of single-use products. The University supports sustainable practices across the campus by encouraging reusable alternatives, especially in dining areas, offices, and events. These efforts include decreasing reliance on single-use items such as cups, plates, and cutlery, and offering reusable options whenever possible. In addition, the University raises awareness about the environmental impacts of single-use products and collaborates with suppliers to minimize packaging waste. These policies are part of the University’s overall commitment to sustainability and waste reduction.
Istanbul Okan University carries out various initiatives across the campus to reduce paper and plastic use. These activities are planned within the framework of its sustainability and Zero Waste strategy.
Kâğıt ve Plastik Kullanımını Azaltma Programı (İstanbul Okan Üniversitesi, Türkiye)
SDG 12.2.7 Disposable policy: extensions to services
Istanbul Okan University’s policies on reducing single-use products, limiting plastic consumption, and improving waste management also comprehensively cover external service providers and the supply chain. The University ensures that its commitment to sustainability and environmental responsibility is reflected not only on campus, but also in its relationships with third-party suppliers and service providers.
By extending these policies to the supply chain and outsourced services, Istanbul Okan University guarantees that its sustainability efforts are comprehensive and integrated across all operations.
Zero Waste Regulation (Official Gazette No. 30829):
As part of Turkey’s national waste management strategy, Istanbul Okan University ensures that its suppliers and contractors comply with waste reduction strategies. This regulation obliges institutions to implement waste reduction and recycling practices and provides a legal basis for ensuring that suppliers follow these rules and contribute to the University’s zero-waste goals.
SDG 12.2.8 Minimisation policies extended to suppliers
Istanbul Okan University’s policies on reducing single-use products, limiting plastic consumption, and improving waste management also apply to outsourced suppliers that provide equipment, stationery, and construction-contract services. To ensure that its sustainability and environmental policies are integrated at every stage of the supply chain, the University implements the following measures:
By extending these policies to suppliers providing equipment, stationery, and construction contracts, Istanbul Okan University guarantees that its environmental initiatives are comprehensive and influence all procurement and service-delivery processes, thereby spreading sustainability throughout the entire supply chain.
Zero Waste Regulation (Official Gazette No. 30829):
As part of Turkey’s national waste management strategy, Istanbul Okan University ensures that its suppliers and contractors comply with waste-reduction strategies. This regulation obliges institutions to implement waste reduction and recycling practices, and it provides a legal basis for ensuring that suppliers follow these rules and contribute to the University’s zero-waste goals.
SDG 12.3 Proportion of recycled waste
SDG 12.3.1 Waste tracking
Istanbul Okan University measures the amount of waste generated and recycled across the University. As part of its sustainability initiatives, the University is committed to monitoring waste outputs, with a focus on reducing overall waste volumes, increasing recycling rates, and minimizing contributions to landfills. This measurement process includes the regular tracking and reporting of waste data, which helps the University assess its environmental impact and make informed decisions to improve waste management practices and sustainability performance.
Waste Management Regulation (No. 29314):
The Waste Management Regulation defines the responsibilities of businesses, suppliers, and contractors for managing and disposing of waste. The regulation requires waste to be separated at the source, encourages recycling, and provides guidelines for the proper disposal of hazardous materials. Istanbul Okan University’s requirement that its suppliers and contractors comply with its waste disposal policies is consistent with this regulation.
**
Sıfır Atık Yönetim Sistemi (Türkiye Cumhuriyeti Çevre, Şehircilik ve İklim Değişikliği Bakanlığı)

SDG 12.3.2 Proportion of waste recycled
Istanbul Okan University carries out sustainable management practices for food waste, organic waste, and waste oil generated on campus.
Plant Waste: Leaves, garden trimmings, and other plant-based wastes collected across the campus are composted and then delivered to local farmers to be used as organic fertilizer. This practice supports both sustainability and collaboration with the community.

Waste Oil: Used cooking oils generated in campus cafeterias and dining areas are collected by a licensed company and properly recycled, helping to prevent environmental pollution.
 |  |
Food Waste: Istanbul Okan University operates a structured process to systematically monitor, control, and sustainably manage food waste generated across the campus. At all food production points of the University, daily leftover meals are separated from other waste streams and collected in special containers. By periodically reporting food-waste quantities, the University contributes both to reducing food waste and to making production planning more efficient.
Collected food waste is inspected by authorized personnel in accordance with the University’s procedures. Only food that is safe for consumption, unspoiled, and poses no risk is approved for feeding campus animals. Approved leftovers are then delivered through a controlled distribution system to designated feeding points determined by the Animal Rights Club and authorized staff. This practice ensures that campus animals are fed regularly and safely, while also reducing the environmental impacts of food waste and supporting the University’s sustainability goals.

Additionally, thanks to the regular measurement and record-keeping practices carried out in meal production units, improvement steps aimed at reducing food waste (such as portion optimization, menu planning, effective stock management, etc.) are systematically evaluated. This comprehensive monitoring mechanism constitutes a concrete part of the efforts conducted in line with the University’s zero-waste, green campus, and sustainable food management goals.
These initiatives are part of our broader commitment to sustainability; we continuously aim to reduce food waste across the University and to encourage more efficient use of resources.
SDG 12.4 Publication of a sustainability report
SDG 12.4.1 Publication of a sustainability report
Legal Basis for the Policies
Istanbul Okan University bases its policies on minimizing the use of single-use products, reducing plastic consumption, and regulating waste management on national and international legal frameworks that focus on environmental protection, sustainability, and public health. These legal bases ensure the University’s compliance with regulations and reflect its commitment to environmental responsibility.
1. Turkish Environmental Law (No. 2872):
The University’s policies are aligned with the Turkish Environmental Law, which envisages minimizing waste generation and encouraging recycling. Article 11 of the law promotes the reduction of solid waste through sustainable practices and the safe disposal of hazardous waste. The law also supports the reduction of plastic waste and aims to prevent the use of non-recyclable materials; this provides a strong legal foundation for the University’s plastic minimization efforts.
2. Zero Waste Regulation (Official Gazette No. 30829):
In line with the “Zero Waste Regulation,” which is part of Turkey’s Zero Waste Initiative launched in 2019, Istanbul Okan University has adopted policies to minimize single-use products and promote waste recycling. This regulation requires institutions to implement waste management systems aimed at reducing the amount of waste sent to landfills and mandates the collection and segregation of recyclable materials. It also encourages the minimization of single-use plastics, in line with the University’s sustainable plastic-reduction policies.
3. Regulation on the Control of Packaging Waste (Official Gazette No. 28035):
This regulation aims to minimize the environmental impact of packaging waste, including plastic packaging, and encourages the reduction, reuse, and recycling of materials. Istanbul Okan University follows these guidelines through its plastic minimization and waste disposal policies by actively promoting the use of reusable and recyclable materials on campus.
4. Occupational Health and Safety Law (No. 6331):
The University’s policies regarding the disposal of hazardous waste—especially in laboratories and other high-risk areas—are based on the Occupational Health and Safety Law. This law requires the safe management and disposal of hazardous materials to protect public health and workplace safety, providing a legal ground for proper waste management systems.
5. EU Single-Use Plastics Directive (Directive 2019/904):
Although not directly binding, Istanbul Okan University’s policies are influenced by international standards such as the EU Single-Use Plastics Directive. This directive encourages member states to adopt sustainable alternatives and reduce single-use plastic products such as straws, cutlery, and food containers. The University’s efforts to reduce plastic use are consistent with these global best practices.
6. Paris Agreement (2015):
As part of global efforts to combat climate change, Istanbul Okan University’s policies contribute to Turkey’s commitments under the Paris Agreement. By reducing waste, minimizing plastic use, and promoting recycling, the University supports the reduction of carbon emissions, prevents environmental degradation, and advances sustainable development goals.
7. Turkish Waste Management Regulation (No. 29314):
The University’s waste disposal policies are also in compliance with the Turkish Waste Management Regulation, which governs the collection, transportation, and disposal of waste, including both hazardous and non-hazardous materials. This regulation emphasizes reducing waste at the source and encourages recycling initiatives—key elements of the University’s waste management strategy.
By adopting policies grounded in national and international legal frameworks, Istanbul Okan University ensures compliance with laws and strengthens a culture of sustainability and environmental management. The University is committed to continuous improvement in these areas and aims to contribute to a healthier and more sustainable future.